Add Points
InkScribe
InkScribe Tool
PathScribe Panel
AG Utilities Live Effects
Illustrator Location:
Advanced Toolbar > Pen Stack > InkScribe Tool
The InkScribe tool appears in Illustrator’s main toolbar (which must be in Advanced mode: View > Toolbars > Advanced), stacked under the native Pen tool. As with other stacked tools, click and hold on the top tool icon to display the tools stacked under it.
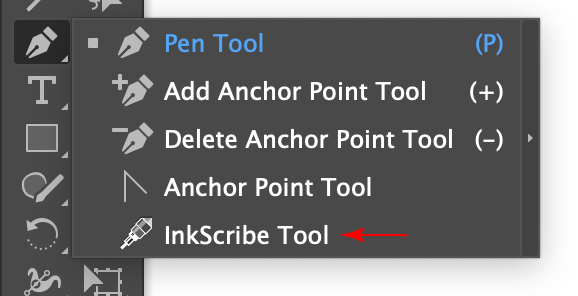
InkScribe Tool Location
The InkScribe tool’s primary cursor looks like the end of a technical pen, and can have badges and additional forms:

InkScribe Tool Cursors
Illustrator Location:
Advanced Toolbar > Pen Stack > InkScribe Tool
Whether starting a new path or continuing an existing path, the type of anchor point (corner or smooth) that the InkScribe tool creates depends on several factors. If the new point is simply created through a click (with no drag), then the point’s type is determined by the button which was selected in the InkScribe panel or virtual panel:
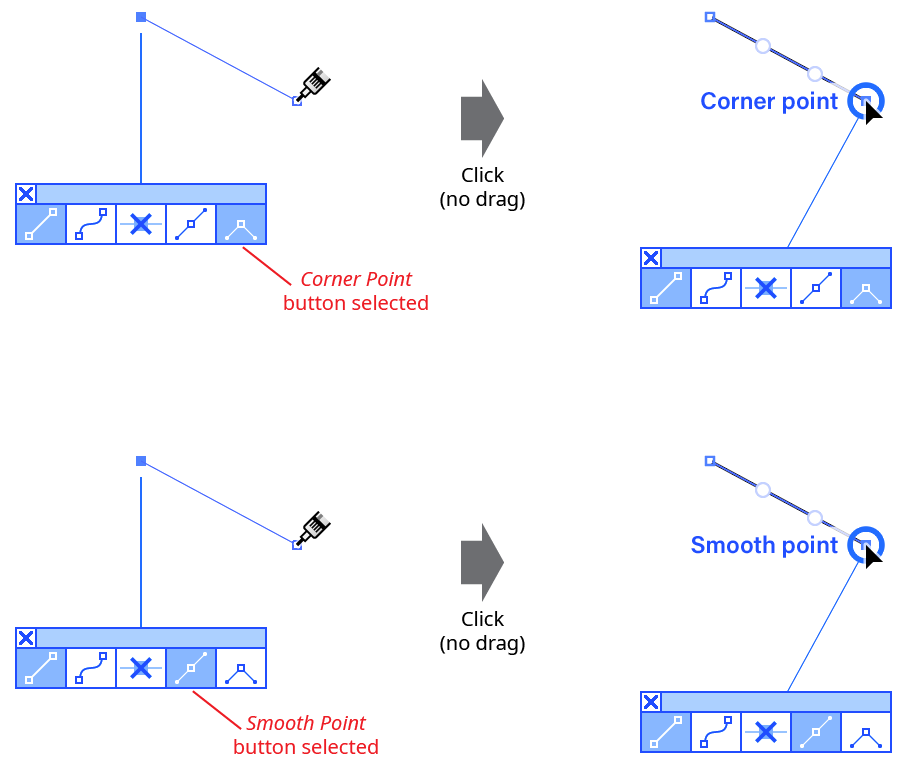
InkScribe New Point Type
If the point is created by dragging, then it will always be made smooth type, unless the Option/Alt key is pressed and the tool preference Option/Alt-Drag a Point to is set to Define Out Handle (the default); then the resulting point will always be made corner type.
When dragging to create a new point, and thereby creating two handles, several keys can be pressed:
Shift: Constrains handle angles to 45° increments around the general constrain angle.
Option/Alt: Defines the Out handle (if the tool preference Option/Alt-Drag a Point to is set to Define Out Handle; or constrains the handle lengths to multiples of the Distance Factor (if the tool preference Option-Alt-Drag a Point to is set to Constrain Distance by Factor). When defining the Out handle, if the
Option/Altkey is released and the cursor moved again, the handles will be made 180° opposed again.Command/Ctrl: Locks the In handle length to the value it had when the key was first pressed.
Space: Moves both the handles and anchor point as one.
Tab: Switches the last segment between curved and straight.
Illustrator Location:
Illustrator Main Menu > Window > Astute Graphics > PathScribe
When no handles are selected, the panel appears in Point Mode:
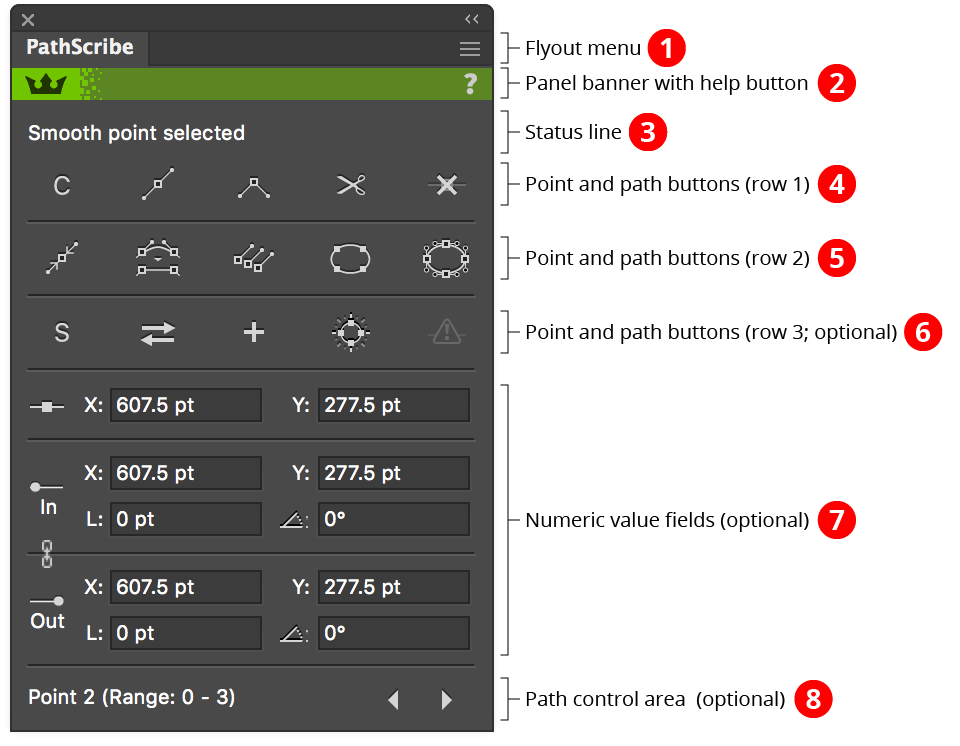
PathScribe Panel point mode
1. Flyout menu
See PathScribe Panel: Flyout Menu.
2. Panel banner
The help button on the right opens the help documentation in the Astute Manager. If this does not automatically appear, please ensure your Astute Manager is running first.
Click on the other area of the color bar to activate the PathScribe tool. This is a quick method of locating the tool within the default Advanced toolbar or a custom toolbar.
3. Status Line
Shows information about the current selection, for example “7 points selected”. When exactly two anchor points are selected, the status line shows the distance between them, and displays a small button which allows you to average the points’ positions, to make them coincident:

PathScribe Panel two point average
Option/Alt-clicking on the status line when showing the distance between two points will copy the distance value to the system clipboard.
If the third row of buttons is hidden, the status line also contains a redundant point indicator/button (see below). Finally, the status line will also indicate what you are editing during a drag operation.
4. Point and Path Buttons (row 1)
a. Connector Point Recognition Button: Toggles Connector Point recognition. When the “C” symbol is dim, connector point recognition is off and the PathScribe tool will not afford any special handling to points which qualify as connectors.
b. Smooth Point Button: Changes all selected anchor points to smooth points. By default, this also adds new handles to these points so they all have two opposed handles. This can be very useful for creating a path that runs smoothly through the points:
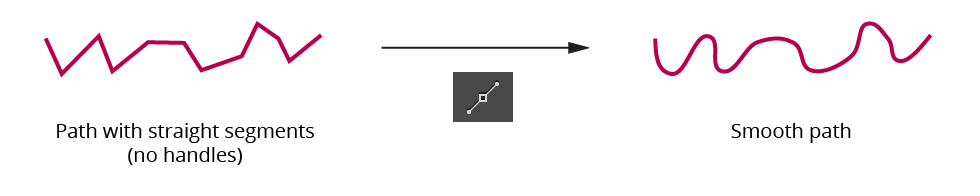
PathScribe smooth point button example
The algorithm that PathScribe uses to create new handles is as follows: If a point already has one handle, its second handle is created by mirroring the existing handle. If a point has no handles, the new handle angle is calculated by bisecting the angle formed by the previous point, the point in question, and the next point, and taking its perpendicular. The new handle length is calculated by taking the lesser of the distances from the point in question to the previous and next points, and multiplying by the smoothing ratio (set in the Preferences dialog). Handles of endpoints of open paths, if created, are adjusted to aim towards the next/previous handle.
To change selected anchor points to smooth points without adding handles, hold down Option/Alt when clicking the button.
c. Corner Point Button: Changes all selected anchor points to corner points. No handles are created or changed.
d. Split Path Button: Splits the path(s) at the selected points, just as clicking on them with the Scissors tool would. Both new endpoints get a copy of the original point’s handles.
e. Smart Remove Point Button: Removes the selected point(s) from the path while attempting to keep the curve as close as possible to its original shape. This is achieved by adjusting the lengths (but not angles) of the handles on either side of the removed points. To remove points without handle adjustment in the manner of the Delete Anchor Point tool, hold down Option/Alt while clicking the button.
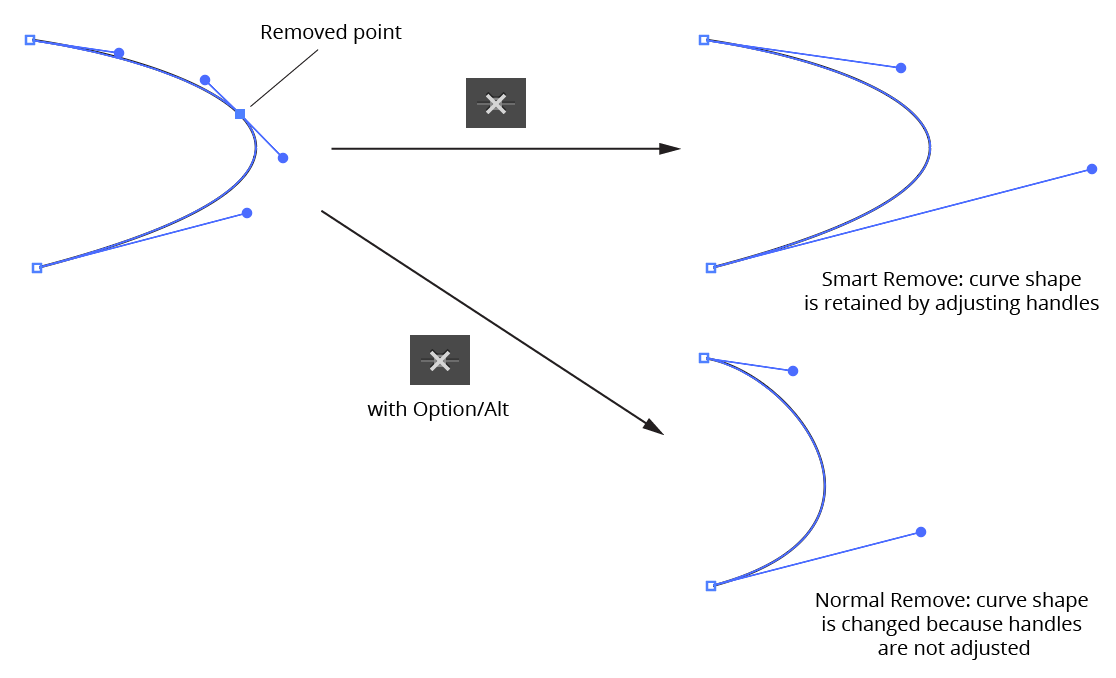
PathScribe Panel smart point remove
When anchor points are selected, you can use the keypress assigned in the Keyboard Shortcuts dialog for “Increase Diameter” (by default, the right bracket key – ]) as a shortcut for the Smart Remove Point button.
When Shift is held down while the button is clicked, PathScribe removes straight segment corners. To utilize this function, two or more adjacent anchor points must be selected, the first and last of which are adjacent to a straight segment (or at the end of an open path); the segments do not necessarily have to form a “nice” corner. The selected anchor points are replaced by a single anchor point at the intersection of the outer straight segments:
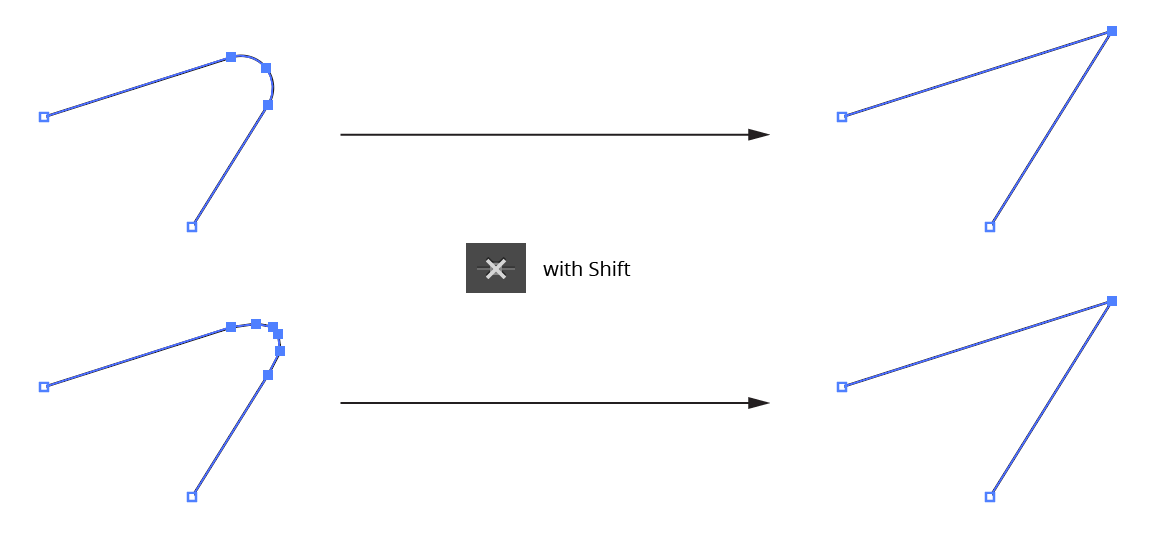
PathScribe removes handles
5. Point and Path Buttons (row 2)
a. Retract Handles Button: Retracts all of the handles on the selected point(s). Point types are not changed. Holding down Option/Alt while clicking the button activates an alternate function: it swaps the positions of the in and out handles on each selected point.
b. Retract Segment Handles Button: Retracts handles from all selected path segments. Point types are not changed.
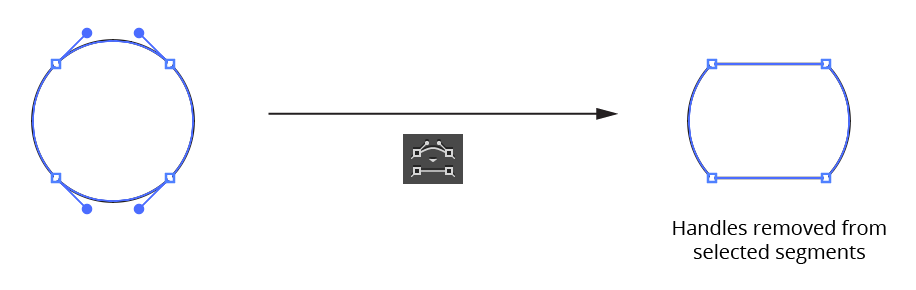
PathScribe Panel remove handles from segments
c. Show Handles Button: All paths or compound path subpaths which are at least partly selected will have all handles made visible (note that this deselects all anchor points and instead selects all path segments).
d. Select Path Points Button: Selects all points on all paths which are at least partially selected.
e. Select All Handles Button: Selects all handles on all paths which are at least partially selected; PathScribe then enters Multi-Handle mode.
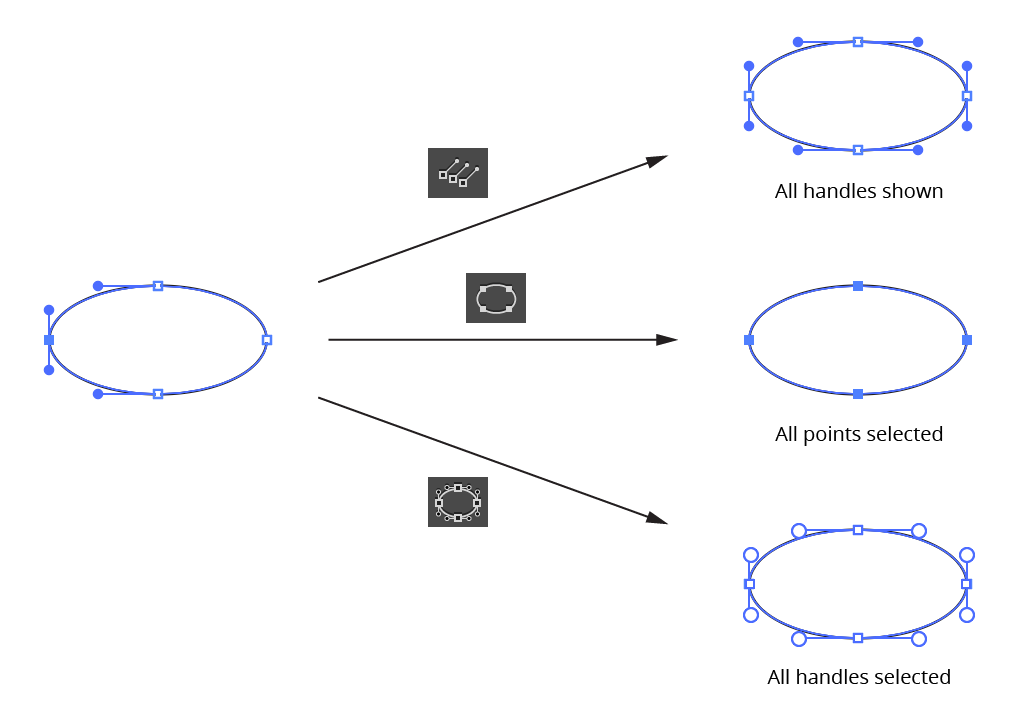
PathScribe second row icons
6. Point and Path Buttons (row 3)
This row can be shown or hidden using the PathScribe panel flyout menu.
a. Smart Smooth Button: Enables or disables “Smart Smooth”, a feature of the PathScribe tool which allows you to convert a corner point into a smooth point simply by dragging one of the point’s handles to be opposite the other (within a certain tolerance). A small red “S” annotation is drawn over points which are being aligned this way. The threshold angle value can be specified in the Preferences dialog.
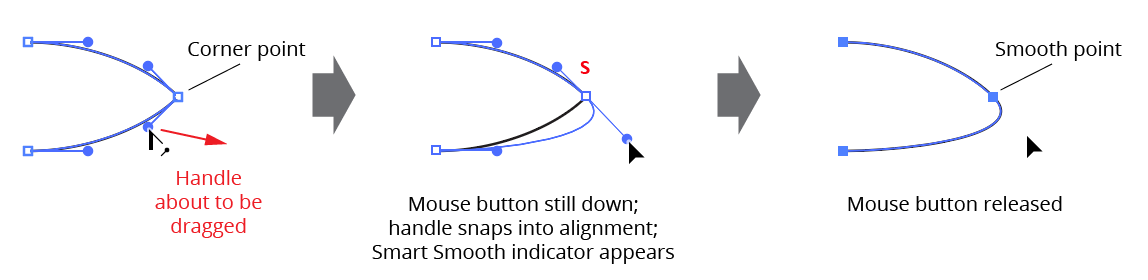
PathScribe panel smart smooth
b. Reverse Path Direction Button: Reverses the direction of any selected paths or subpaths. This will generally only produce a visible change to the artwork if a subpath of a filled compound path is reversed or if the path is being stroked by an asymmetric brush:
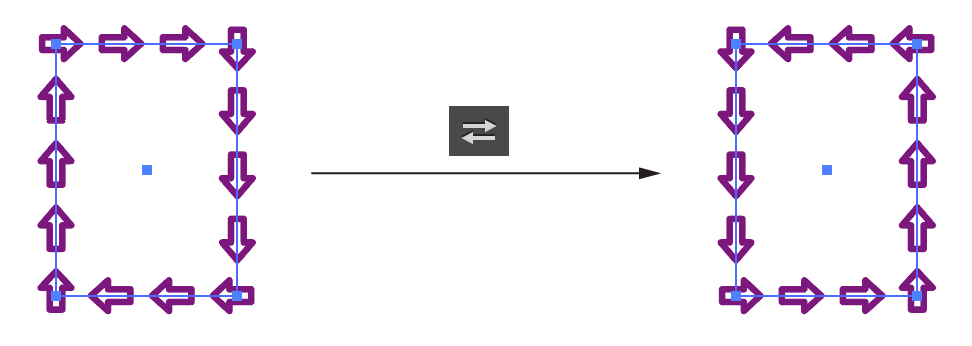
PathScribe Reverse Path Direction Button
When the third row of buttons is hidden, the “Reverse Path” command can still be accessed through the PathScribe panel flyout menu (see below).
c. Add Points to Selected Segments Button: Adds anchors points to every selected segment of every selected path. The number of points added and algorithm used to add them are taken from the last-used settings. To open the dialog which enables you to edit these values, Option/Alt-click on the button.
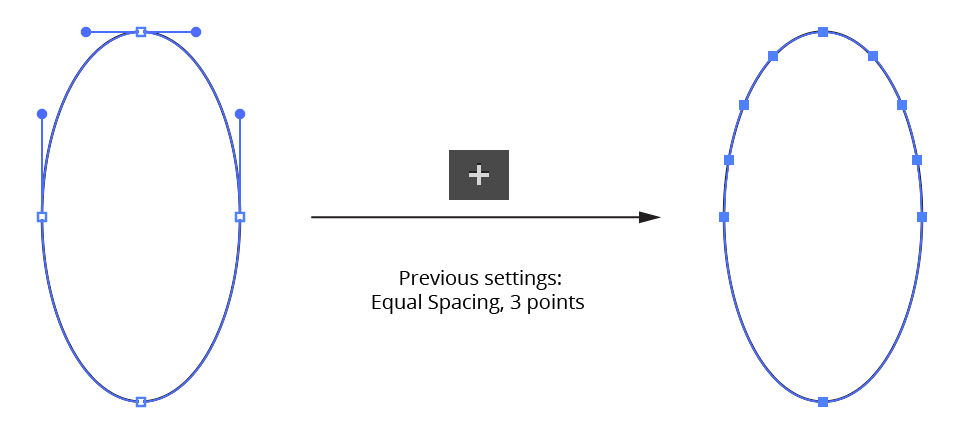
PathScribe Add Points to Selected Segments Button
When the third row of buttons is hidden, the “Add Points” command can still be accessed through the PathScribe panel flyout menu (see below).
d. Move Points to Tangencies Button: Moves anchor points on the selected paths to positions along the path where the angle of the path as it passes through the anchor point is tangent to the horizontal or vertical axes (taking into account the current constrain angle).
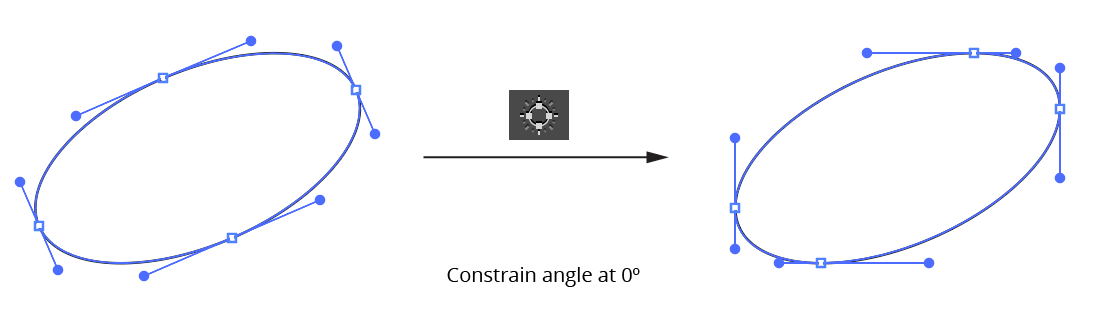
PathScribe Move Points to Tangencies Button
Holding down Option/Alt when clicking the button changes its functionality: new anchor points are placed at the tangent positions, but the existing anchor points are retained.
Holding down Shift when clicking the button also changes its functionality: Only selected points are moved to tangencies.
When the third row of buttons is hidden, the “Move Points” command can still be accessed through the PathScribe panel flyout menu (see below).
e. Remove Redundant Points Button: Removes all redundant points from all selected paths. If the button is disabled (dim), no redundant points exist. A redundant point, also known as a doubled point, is defined as the latter of two consecutive anchor points on a path that have exactly the same X and Y coordinates and don’t have handles in the (zero-length) segment between them. They are often created after using the PathFinder functions or after using Object > Path > Outline Stroke, and despite not changing the shape of the path, can cause problems when performing additional functions such as offsetting. You can highlight the locations of redundant points when using the PathScribe tool by enabling the corresponding preference (see PathScribe Preferences).
When the third row of buttons is hidden, the button will appear on the right side of the top status line. Due to space considerations, the icon uses a small exclamation point rather than the full icon:
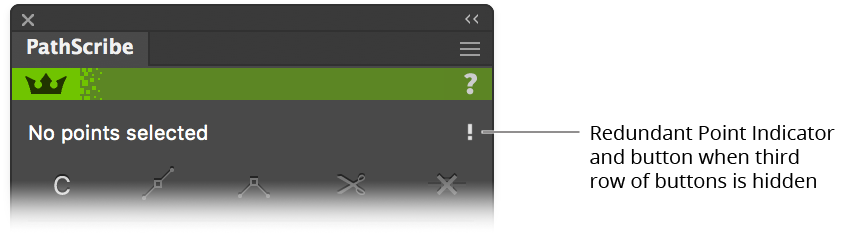
PathScribe Remove Redundant Points Button
7. Numeric Value Fields
This area can be shown or hidden using the PathScribe panel flyout menu.
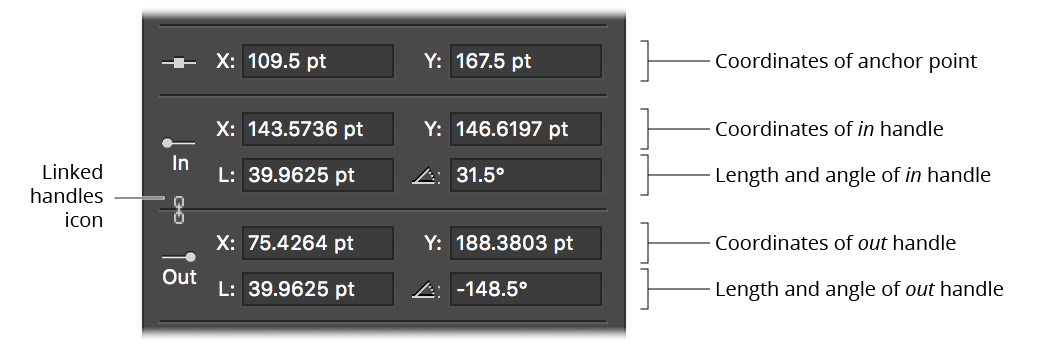
PathScribe Numeric Value Fields
When an anchor point is selected, the numeric value fields becomes active, reflecting the X and Y coordinates of the anchor point and the coordinates, lengths and angles of its two direction handles. You can make edits to any of the fields by simply typing in a new value and pressing Return/Enter or Tab. Like other numerical entry fields in Illustrator, you can use any units you wish (except in the angle fields) and one math operator.
The linked handles icon appears when editing a smooth point, as a reminder that edits to the coordinates or angle of one handle will also affect the other handle (if it exists).
You can specify the number of digits that are displayed after the decimal point through PathScribe’s Precision preference.
When more than one anchor point is selected, fields which are blank indicate that multiple values are present. You can still type a new value into the field, thereby assigning it to all selected anchor points/ handles. Or, for the anchor point fields, you can Shift-click on the anchor point icon to average all values in both fields; or Shift-click on the “X:” or “Y:” labels to average only the corresponding value.
When the Show Anchor Point Coordinate Ranges preference is enabled, mixed values will be instead displayed in the anchor point coordinate fields as a value (in blue) representing the difference between the highest value and the lowest value:
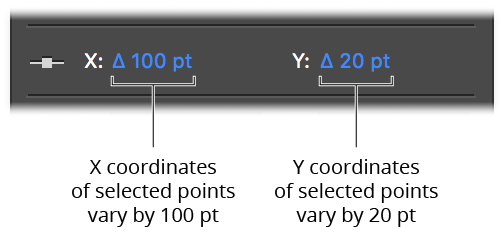
PathScribe Coordinates of points
Clicking on the range will allow you to enter a new value, just as with the preference disabled. Values which are too small to display with the current precision are displayed using scientific notation, e.g. 3.12E-06, where “E-06” means “×10–6” (one-millionth).
8. Path Control Area
This area can be shown or hidden using the PathScribe panel flyout menu. In Point Mode, the path control area has three different appearances:
a. When the selection consists of more than one path, the path control area shows the total number of selected paths and the number of each type (closed, open, or single-point). Each subpath of a compound path is reported separately.
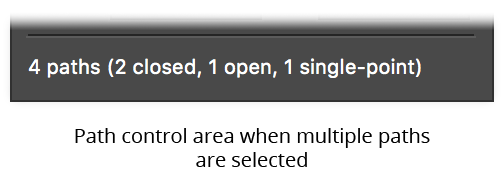
PathScribe Panel Path Control Area multiple paths
b. When the selection consists of a single path, and either multiple points or no points on the path are selected, the status line shows the type of path and a Select Point 0 button. Because Illustrator numbers points starting at zero and continuing consecutively in the direction of the path, clicking the button will therefore select the first point on the path. By default, the selected point will be briefly highlighted with a small magenta dot to make it easier to locate. If the Highlight Panel-Selected Points preference is disabled, you can still highlight the point on a use-by-use basis by holding down Option/Alt when clicking the button.
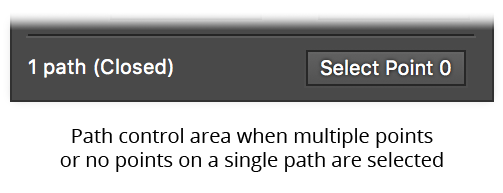
PathScribe Panel Point Control Area Show Point
c. When the selection consists of a single point on a single path, the path control area shows the index of the point, the range of indices on the path, and two buttons that let you change the point that is selected. To move to (i.e., select) the previous or next point on the path, click the Previous point or Next point button. Clicking the Next point button or Previous point button while the last point of an open path is selected will wrap around to the other end.
Holding down Shift while clicking the Next point or Previous point buttons will move ahead or back 10 anchor points (if the path has more than 10 points).
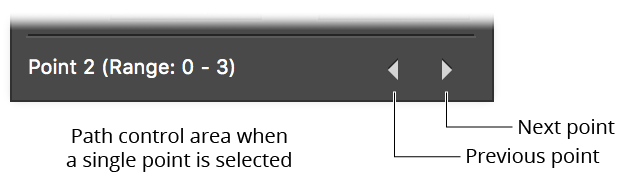
PathScribe PCA Previous Next buttons
Again, the selected point will be briefly highlighted by default.
Illustrator Location:
Illustrator Main Menu > Effect > AG Utilities > ...
Add Points is an Astute Graphics live effect for paths that adds anchor points to paths, similar to the functionality of the “Add Points” function of the PathScribe panel. By itself, adding points is not particularly useful, as the look of the art won’t change; the real power comes by stacking the live effect with other live effects that operate on or depend on anchor point placement.
As with most live effects, Add Points appears in the main menu, under Effect > AG Utilities. It can also be applied directly from the Appearance panel using the “Add New Effect” button at the bottom of the panel.
Add Points Parameters Dialog
After applying the live effect using the menu item (or when clicking on the existing effect in the Appearance panel to edit it), the parameters dialog will appear:
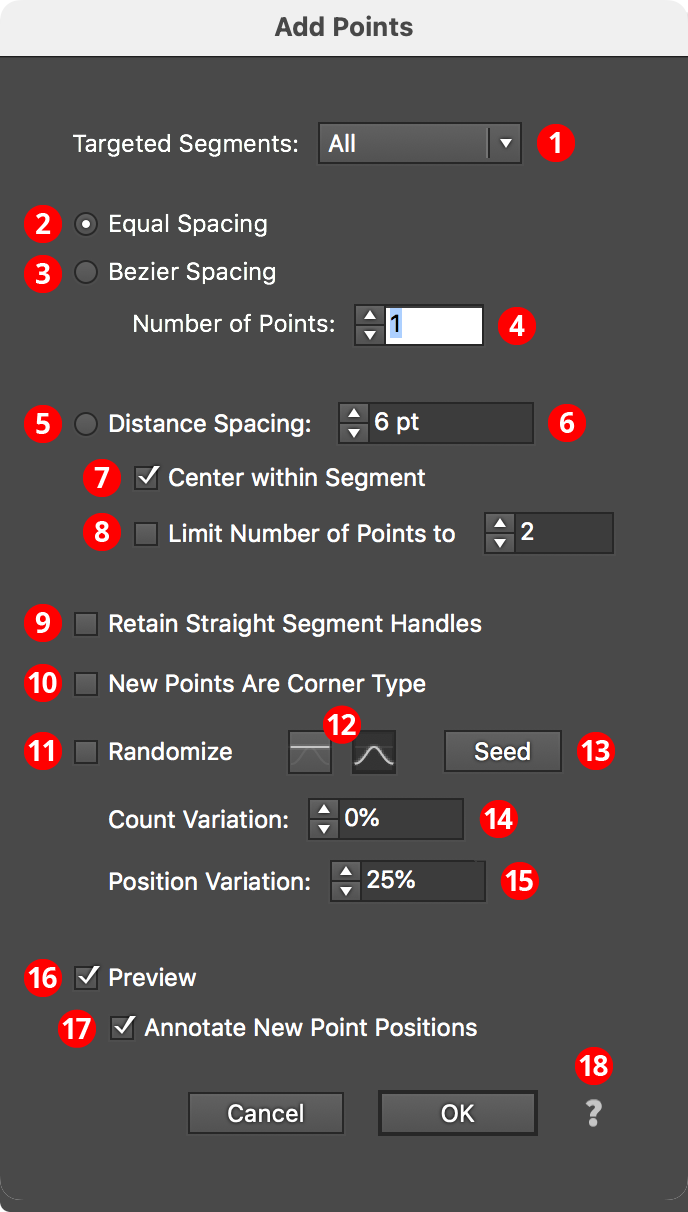
Add Points Parameters Dialog
1. Targeted Segments
By default, all segments in the path have points added to them, but this can be changed to First, Last, Even Only, Odd Only, Curved Only, or Straight Only segments. Even and odd refer to the index number of the segment, which starts at zero for the first segment in the path.
2. Equal Spacing Mode
In this mode, points are added such that the space between them (as measured along the path) is equal.
3. Bezier Spacing Mode
In this mode, points are added such that the cubic bezier t parameter is equally spaced. Generally, this adds more points to areas along the segment which are more tightly curved.
4. Number of Points
For Equal Spacing and Bezier Spacing modes, specifies the number of points to add along each segment.
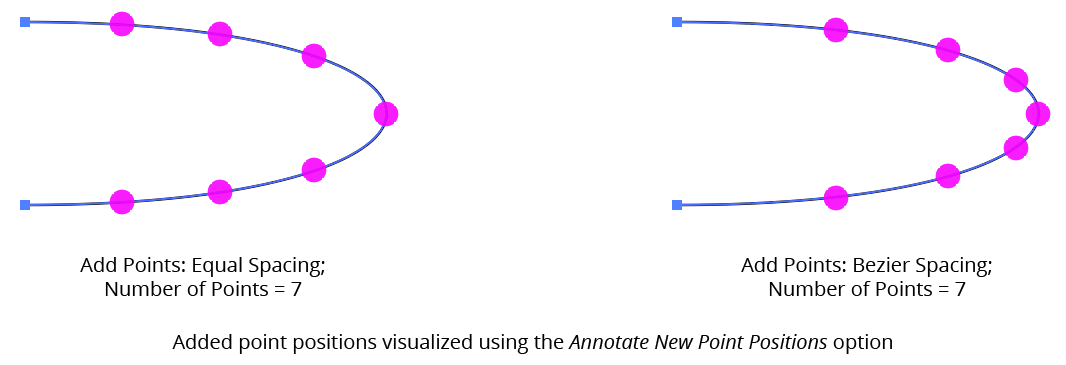
AG Utilities Live Effects - Add Points Equal or Bezier Spacing
5. Distance Spacing Mode
In this mode, points are added equally spaced along the path with the distance specified, adding as many as will fit along the segment unless Limit Number of Points is also enabled.
6. Distance Value
The distance between the added points when using Distance Spacing mode. If the distance value is greater than the segment’s length, no points will be added to the segment.
7. Center Within Segment
In Distance Spacing mode, causes the added points to be centered within the segment, so the distances from the segment’s ends to the first or last added point will be equal (but may not match the specified distance).
8. Limit Number of Points
In Distance Spacing mode, specifies the maximum number of points to add along each segment.

AG Utilities Live Effects - Add Points Distance Spacing
9. Retain Straight Segment Handles
Normally, when anchor points are added to a handleless straight segment, the new points have their handles removed. However, enabling this setting causes the handles to be retained, which can be useful when the new anchor points are subsequently moved and a smooth curve is desired.
10. New Points Are Corner Type
Forces the added points to have corner type rather than smooth. This does not change any handles that the point might have, only the point type.
11. Randomize
Allows for random variation in the count and/or position of the new points.
12. Distribution Curves
Specifies either a linear distribution in random values (all values in the range are equally likely to be chosen) or a Gaussian distribution (central values in the range are more likely to be chosen).
13. Seed
Each random seed number leads to a different sequence of random values. Clicking the button picks a new seed, thereby changing the look of the artwork. To view or specify the seed number directly, Option/Alt-click the button. This lets you recreate a previously-generated look.
14. Count Variation
Specifies the random variation in the added point count (valid for Equal Spacing and Bezier Spacing modes only). For example, if the count is set to 20, then a variation value of 25% would produce count values that vary by as much as 20 × 25% = 5, that is, between 16 and 20; a variation value of 100% would produce count values between 1 and 20.
15. Position Variation
Specifies the random variation in the final positions of the added points.
16. Preview
As with all live effects, when enabled, changing a parameter will immediately update the artwork while the dialog is still open.
17. Annotate New Point Positions
When enabled, the positions of the added points will be temporarily displayed using magenta dot annotations, which is useful if subsequent live effects have not been added to the artwork yet, because by itself, Add Points will produce no visual change to the art.
18. Help Button
Opens the help documentation in the Astute Manager. If this does not automatically appear, please ensure your Astute Manager is running first.